![[LogoShip]](logo5.png)
Software for Windows
Science with your Sound Card!
Features:
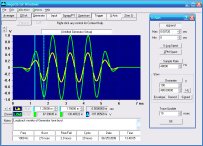
Oscilloscope
Spectrum Analyzer
8-Channel
Signal Generator
(Absolutely FREE!)
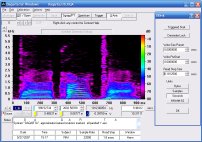
Spectrogram
Pitch Tracker
Pitch-to-MIDI
DaqMusiq Generator
(Free Music... Forever!)
Engine Simulator
LCR Meter
Remote Operation
DC Measurements
True RMS Voltmeter
Sound Level Meter
Frequency Counter
Period
Event
Spectral Event
Temperature
Pressure
MHz Frequencies
Data Logger
Waveform Averager
Histogram
Post-Stimulus Time
Histogram (PSTH)
THD Meter
IMD Meter
Precision Phase Meter
Pulse Meter
Macro System
Multi-Trace Arrays
Trigger Controls
Auto-Calibration
Spectral Peak Track
Spectrum Limit Testing
Direct-to-Disk Recording
Accessibility
Data Logger
Waveform Averager
Histogram
Post-Stimulus Time
Histogram (PSTH)
THD Meter
IMD Meter
Precision Phase Meter
Pulse Meter
Macro System
Multi-Trace Arrays
Trigger Controls
Auto-Calibration
Spectral Peak Track
Spectrum Limit Testing
Direct-to-Disk Recording
Accessibility
Applications:
Frequency response
Distortion measurement
Speech and music
Microphone calibration
Loudspeaker test
Auditory phenomena
Musical instrument tuning
Animal sound
Evoked potentials
Rotating machinery
Automotive
Product test
Contact us about
your application!
Sine Wave Phase
Phase is the measure of the starting point of one sinusoid relative to another. In the sine wave clock example the reference starting point was the 9 o'clock position, so any wave that starts there is "in phase" with the reference wave. If a wave starts anywhere else, its angle relative to this reference is its "phase angle". A wave that starts at 6 o'clock (cosine) is thus at an angle of 90 degrees relative to the reference sine. The cosine (open dots) reaches 12 o'clock just as the sine (solid dots) hits 9 o'clock to start a new cycle:
In mathematics the 3 o'clock position is always used as the starting point, and everything runs counter-clockwise. Apart from a sign change, the results are the same.
If two identical sinusoids are added together, the result is a sinusoid with twice the amplitude. If the two waves are shifted so that they are 180 degrees out of phase, then the positive portions of one wave will cancel the negative portions of the other and the sum will be zero. At intermediate phase angles, the sum can vary over the range from 0 to 200%. At 120 or 240 degrees, the sum will be the same magnitude as either of the original values, but at an intermediate phase.
See also Sine Wave Basics, Magnitude via Vector Sum, Making Waves via Sine Wave Synthesis
- Back to Sine Wave Basics
- Ahead to Magnitude via Vector Sum
- Daqarta Help Contents
- Daqarta Help Index
- Daqarta Downloads
- Daqarta Home Page
- Purchase Daqarta
Questions? Comments? Contact us!
We respond to ALL inquiries, typically within 24 hrs.INTERSTELLAR RESEARCH:
Over 35 Years of Innovative Instrumentation
© Copyright 2007 - 2023 by Interstellar Research
All rights reserved